B2B vs. B2C: What's the Difference? 9 Key Distinctions Between the Two Business Models
Discover the difference between B2B and B2C with 9 key points. Gain a deeper understanding of these two business models to create a suitable strategy for your business.

1. What is the B2B Business Model?
The B2B (Business-to-Business) business model is a type of commerce where companies sell products or services to other businesses rather than directly to final consumers. Here are some key characteristics of the B2B business model:
- Target Customers: B2B customers are businesses or organizations. Transactions are often more complex and involve more parties than in B2C.
- Sales Process: The B2B sales process is typically longer and has more steps. It includes identifying needs, searching for suppliers, negotiating, signing contracts, and executing the transaction.
- Transaction Value: Transactions in B2B often have a much higher value than in B2C. This is because businesses typically purchase a large quantity of products or services for their operations.
- Customer Relationships: Relationships in B2B are often long-term and require a high level of trust between parties. Businesses often build strategic partnerships to ensure stability and long-term growth.
- Marketing and Sales: B2B marketing focuses on building relationships and providing detailed information about products or services. B2B sales often involve direct meetings, product presentations, and negotiations.
- Sales Cycle: The B2B sales cycle is usually longer and requires more steps from initial contact with a potential customer to finalizing the deal.
Examples of B2B business models include manufacturing companies selling raw materials to other manufacturers, software companies providing solutions to businesses, and business consulting services.

2. B2B Business Models
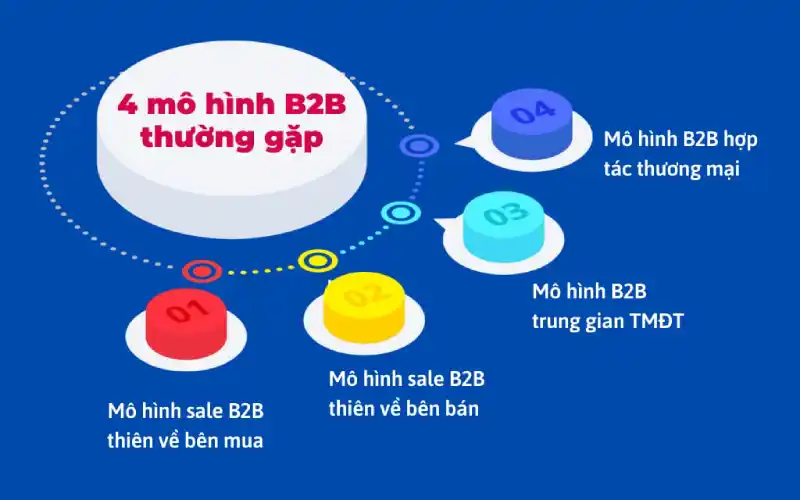
2.1. Seller-Oriented B2B Model
The seller-oriented B2B model is one in which suppliers proactively seek out and provide products or services to other businesses. Characteristics of this model include:
- Proactive Supply: Suppliers often build a list of potential customers and continuously look for sales opportunities.
- Transaction Platform: Companies can use e-commerce platforms or their own websites to showcase products and services, making it easy for other businesses to learn about and place orders.
- Examples: Manufacturers of industrial equipment, raw material suppliers, or software companies selling solutions to businesses.
2.2. Buyer-Oriented B2B Model
The buyer-oriented B2B model is one in which businesses search for and select suppliers to meet their needs. Characteristics of this model include:
- Proactive Search: Buying businesses will actively search for and contact potential suppliers.
- Bidding and Negotiation: There is often a bidding process to select the best supplier based on price, quality, and other conditions.
- Examples: Manufacturing businesses that need to buy raw materials, or retail companies looking for product suppliers to resell.
2.3. Intermediary B2B Model
The intermediary B2B model involves a third party acting as a bridge between the seller and the buyer. Characteristics of this model include:
- Connecting Platform: Online platforms or intermediary service companies help connect suppliers with potential customers.
- Simplified Transactions: The intermediary helps simplify the transaction process, including finding partners, negotiating, and executing the deal.
- Examples: B2B e-commerce sites like Alibaba, or trade brokerage firms.
2.4. Collaborative B2B Commerce Model
The collaborative B2B commerce model is one in which businesses cooperate with each other on a shared platform to create greater value for both sides. Characteristics of this model include:
- Strategic Partnerships: Businesses cooperate to share resources, technology, or markets.
- Creating Shared Value: The goal is to create greater value than by operating individually, often through joint projects, ventures, or partnership programs.
- Examples: Alliances between technology companies to develop new products, or cooperation between businesses to jointly access international markets.
3. What is the B2C Business Model?
The B2C (Business-to-Consumer) business model is a type of commerce where companies sell products or services directly to final consumers. This is the most common model in the consumer market, especially in retail, services, and e-commerce. Here are some key characteristics of the B2C business model:
- Target Customers: Customers in the B2C model are individual consumers who purchase products or services for personal or family use.
- Sales Process: The B2C sales process is typically simple and quick. Customers can search for products, review information, compare prices, and place orders online or in a physical store.
- Transaction Scale: B2C transactions are typically of lower value than B2B and occur more frequently. Consumers usually buy products or services in small quantities.
- Customer Relationships: The relationship between a business and its customers in B2C is often short-term and less interactive than in B2B. However, businesses need to build customer satisfaction and loyalty to encourage repeat purchases.
- Marketing and Sales: B2C marketing focuses on attracting and retaining individual customers through advertising campaigns, promotions, and social media. Marketing strategies often appeal to consumers' emotions and experiences.
- Sales Cycle: The B2C sales cycle is much shorter than in B2B. A consumer's purchase decision is often made quickly and does not require multiple approval steps.

4. B2C Business Models
4.1. Direct Selling
This model involves businesses selling products or services directly to consumers through traditional or online retail channels.
- No Intermediaries: Businesses sell directly to customers without a third party.
- Direct Interaction: Businesses can build direct relationships with customers and gather immediate feedback.
- Examples: Traditional retail stores like supermarkets, clothing stores, and e-commerce sites like the Apple Store, Nike.
4.2. Online Intermediary
This model involves businesses using an online platform to connect sellers and buyers.
- Connecting Platform: Websites or applications that connect consumers with various suppliers.
- Intermediary Fee: The platform typically charges a commission fee on transactions or a subscription fee from sellers.
- Examples: E-commerce sites like eBay, Amazon Marketplace, Shopee.
4.3. Fee-Based B2C
This model involves consumers paying a fee to use a business's products or services.
- Recurring Services: Customers often pay a recurring fee (monthly, yearly) to use the service.
- Long-Term Value: Businesses need to ensure service quality to maintain customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Examples: Subscription services like Netflix, Spotify, or online courses like Coursera, Udemy.
4.4. Community-Based B2C
This model is based on creating and maintaining a community of users around a business's products or services.
- Social Interaction: Businesses create a platform that allows users to connect, interact, and share information with each other.
- Value from the Community: User-generated content and community interaction create value for the entire ecosystem.
- Examples: Social networks like Facebook, Instagram, or online forums like Reddit, Stack Overflow.
4.5. Advertising-Based B2C
This model involves a business providing free content to consumers and earning revenue from advertising.
- Free Content: Consumers don't have to pay to use the service or view the content.
- Revenue from Advertising: Businesses make money by displaying ads to users.
- Examples: News sites like BuzzFeed, video platforms like YouTube, or free ad-supported apps like mobile games.

5. 9 Key Differences Between B2B and B2C
Here is a comparison table of the B2B and B2C business models based on 9 key differences:
Point of Difference | B2B | B2C |
Target Customers | Businesses or organizations. They buy products or services for use in their business operations, production, or to supply to other businesses. | Individual consumers. They buy products or services for personal or family use. |
Negotiation and Transaction Process | More complex, often long-lasting, and involves multiple parties. Businesses must consider many factors like price, contract terms, and support services. | Simple and fast. Consumers can make a purchase immediately without a lot of approval steps. |
Integration Issues | Integrating products or services into a business's system requires high-level customization and technical support, including software integration, management systems, and business processes. | Products or services are typically designed for immediate use without much integration. Consumers just buy and use them directly. |
Marketing Process | Focuses on building long-term relationships and providing detailed, valuable information. Marketing strategies often include webinars, trade shows, and in-depth content marketing. | Aims at consumers' emotions and experiences. Marketing strategies include advertising, promotions, and social media to attract and retain customers. |
Sales Process | Complex and lengthy, often requiring direct meetings, product presentations, and negotiations. Salespeople must have deep knowledge of the product and industry. | Simple and quick. Consumers often buy directly in stores or online. The sales process is less complex and doesn't require many approval steps. |
Order Value and Potential Customer Base | High order value, but the number of potential customers is usually smaller. Transactions often involve large quantities of products or services. | Lower order value, but the number of potential customers is larger. Transactions typically involve small quantities of products or services. |
Sales Cycle Length | A longer sales cycle, which can last from several months to several years, as businesses need time to research, negotiate, and make a decision. | A shorter sales cycle, often completed in a few minutes or days, as consumers typically make purchasing decisions quickly. |
Decision-Making Process | More complex, multi-step, and involves multiple decision-makers. Businesses often have a strict approval process and require the involvement of many departments. | Simple and quick, usually involving only an individual or a family. Consumers can make their own purchasing decisions without approval from many parties. |
Customer Needs | Complex and diverse, requiring customized solutions and technical support to meet each business's specific operational needs. | Simpler, often based on personal preferences and convenience. Consumers look for products or services that fit their individual or family needs. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, while both B2B (Business-to-Business) and B2C (Business-to-Consumer) are forms of commerce, they operate on fundamentally different principles. B2B is characterized by its focus on long-term relationships, complex sales cycles, and high-value transactions tailored to the specific needs of other businesses. In contrast, B2C is driven by individual consumer behavior, focusing on short, quick transactions, emotional appeal, and a broad customer base. Understanding these core differences is essential for businesses to develop effective marketing, sales, and operational strategies that align with their target audience and business objectives.